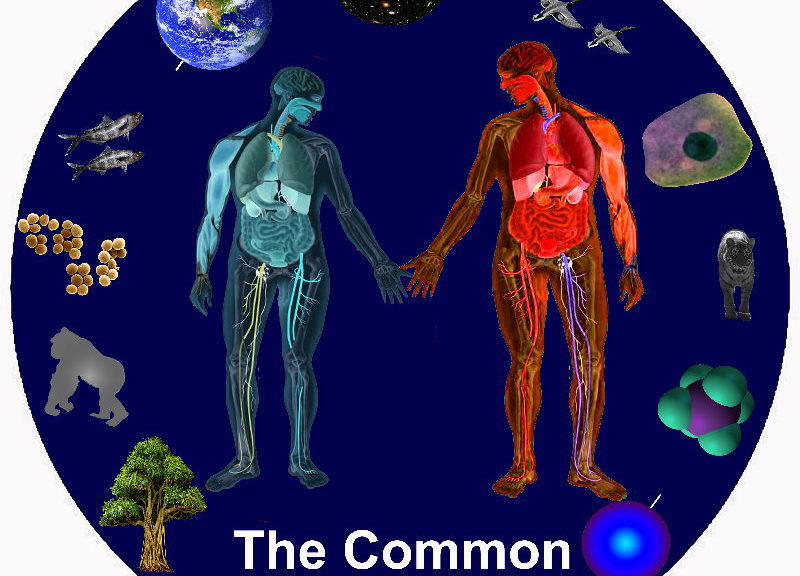
Everything in and around us is made of parts.
The parts organize and bond to each other.
A new whole results.
The”common” in the title refers to the common fact that all matter is made of parts and the parts yearn to bond in an attempt to create a new Oneness.
The “vein” in the title refers to the bonds that brings the organized parts together to the make the new whole. It also hints at a biological and medical focus of the project.
The universal equation that reflects this concept is 1 +1 = 1.
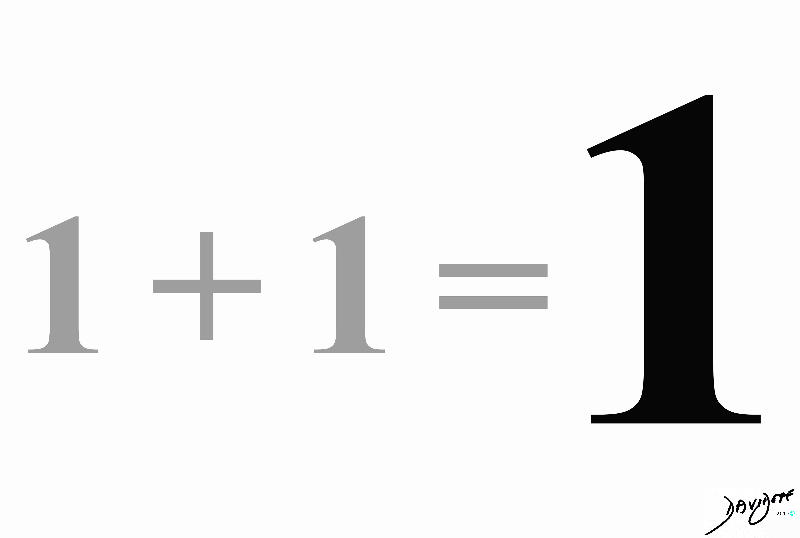
The key element of this equation is that the result is most often surprising and unexpected.
Units to unity is the concept that embodies the 1 + 1 = 1 principle but expressed in words.
Three basic examples are described below; the hydrogen atom, helium, bricks, and fertilization.
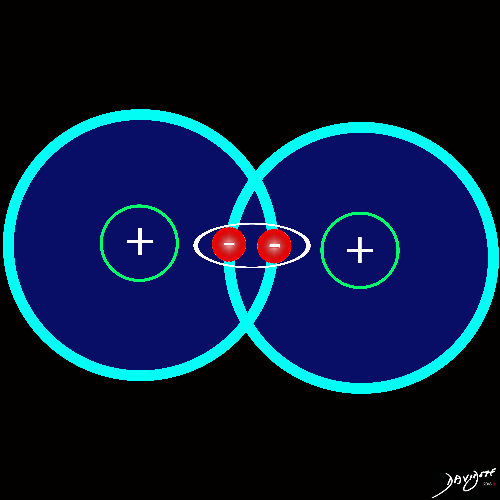
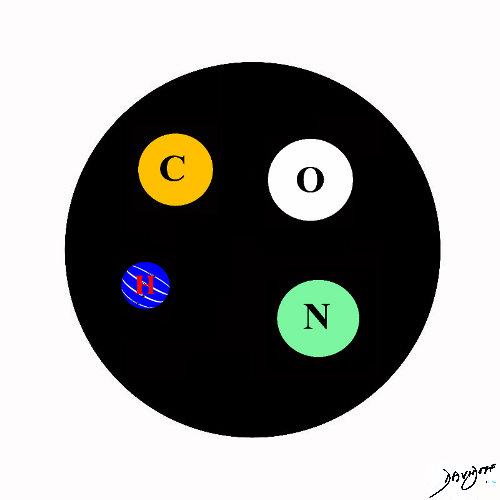
Starting with the Hydrogen Atom
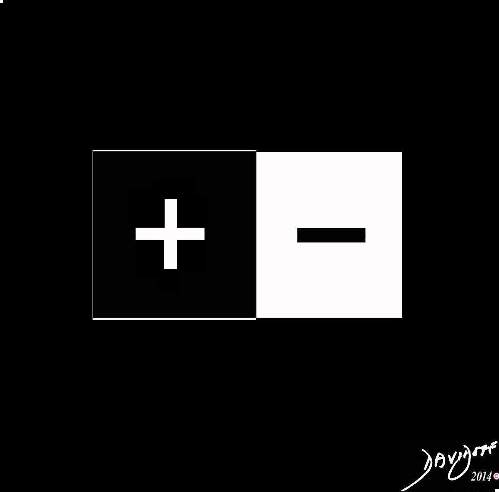
Single Negative Charge and Single Positive Charge
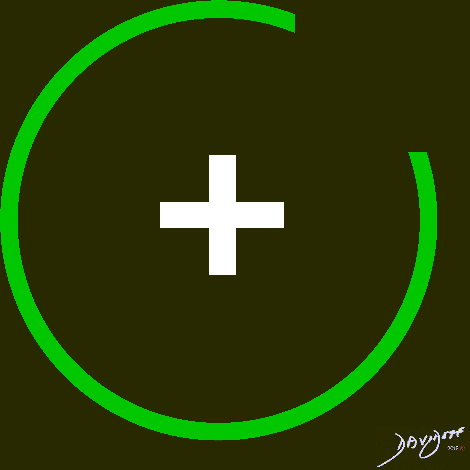
+
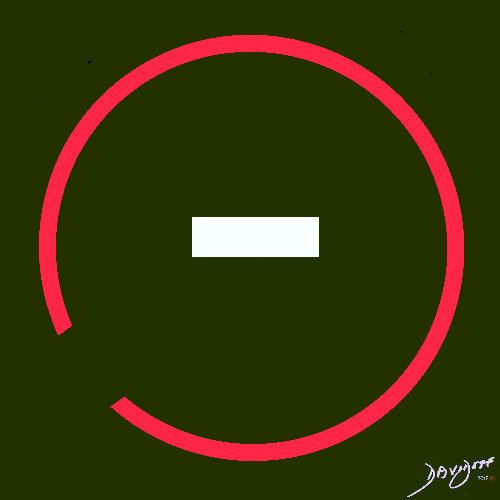
=

=

The Brick and The Common Vein
Building Bricks and Building with Bricks

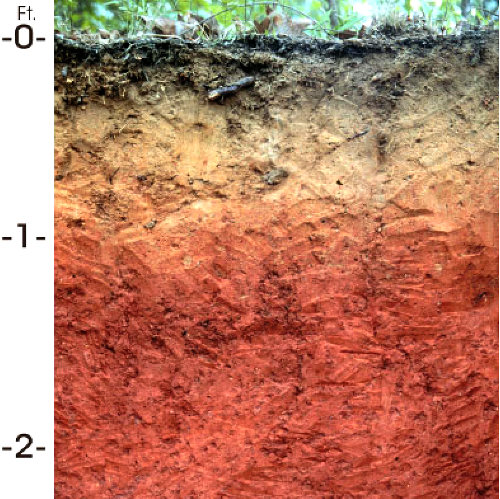
The brick is the basic building block of many structure around us. It is made of many parts of the soil of the earth bound together by cement and created in an extremely hot environment.
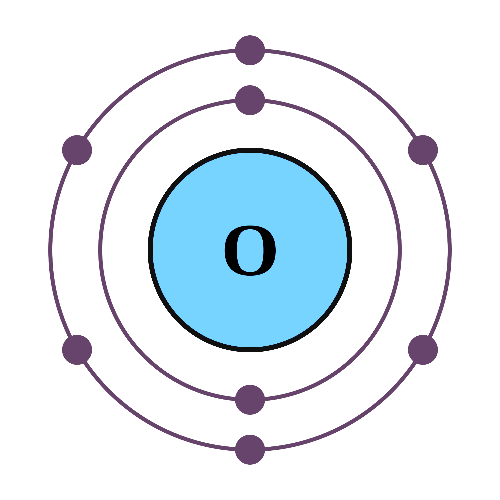
One of the major parts of soil in general and clay soil in this instance, is silicon dioxide (Si02). Si02 is made from 1 part (atom) of Si and 2 parts of oxygen. In the following text, the units to unity principle is applied to Si02, as one of the components that make up the brick.
Atoms

+
+

=
Molecule
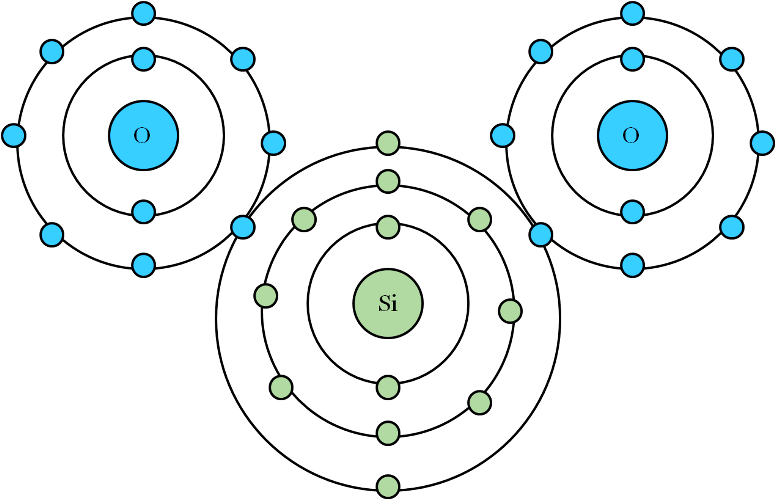
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon and oxygen bond by sharing electrons in their outer shells and thus create a new, molecule called silicon dioxide (Si02). The sharing of the outer electrons (valence electrons) is called covalent bonding.
The Si02 molecules bond with other Si02 molecule with very strong covalent bonds and weaker intermolecular (van der Waal) bonds.
Substance

+

+

=
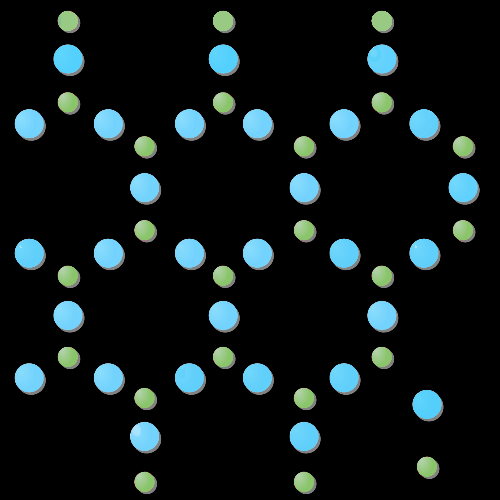
The compound silicon dioxide also known as silica is the second most abundant mineral in the crust of the earth. Silicon dioxide is very hard. These properties result from the very strong covalent bonds that hold the silicon and oxygen atoms in the giant covalent structure.
Silicon dioxide most commonly found in nature as quartz. It is found in granite, and is the major compound of sandstone. The sand on a beach is made mostly of silicon dioxid
Mixture
Bricks are manufactured from clay, which is a mixture of substances including, SiO2 and other clay minerals in the soil. Examples of these minerals include kaolin, smectite, iliite, and chlorite .

+
=

Creating Bricks from the Mixture
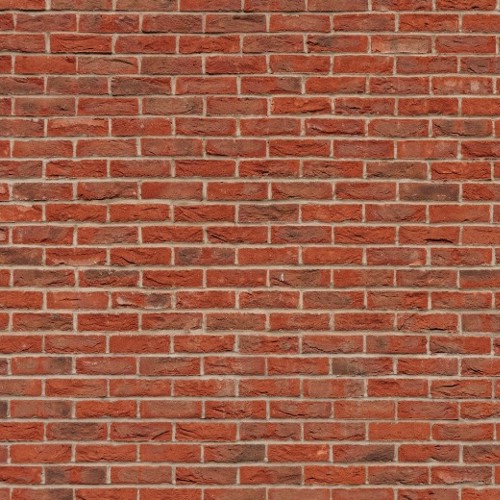
Bricks are made from clay. The clay is bonded by cement (mortar). The mixture is placed in a kiln and is subjected to up to 2,000° F during the firing process. The clay changes form as it dehydrates. The new anhydrous minerals contain interlocking (bonding) networks of mullite crystals, quartz, and some super-cooled liquid (glass). Brick has compressive strength, is durable, demonstrates thermal and sound insulation, is able to withstand severe weather, and is resistant to fire and wear.
The Clinking Sound of Quality Brick
Bricks

+

+

=
Wall

+

+

=
Building
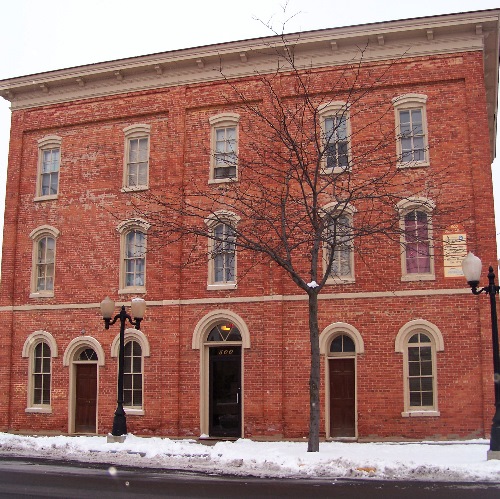

The brick is to the wall, as the wall is to the building.

+

+

=
Town
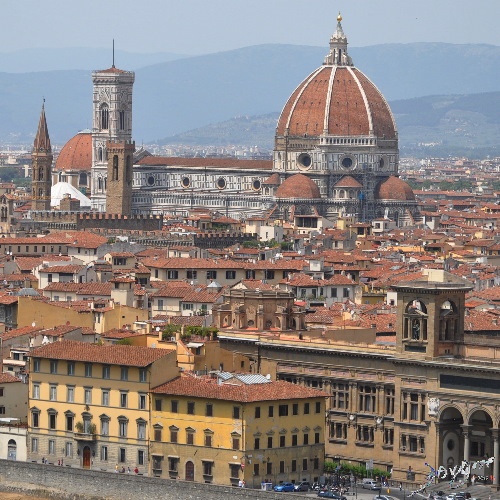

The Cell and the Common Vein
Building the Body Within Us and the Community Around Us
Atoms of the Body

+
+

=
Macromolecules
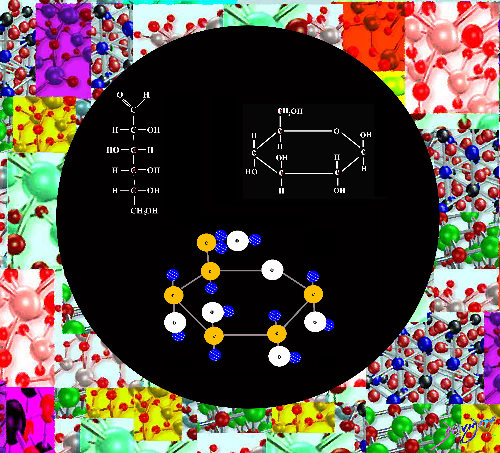
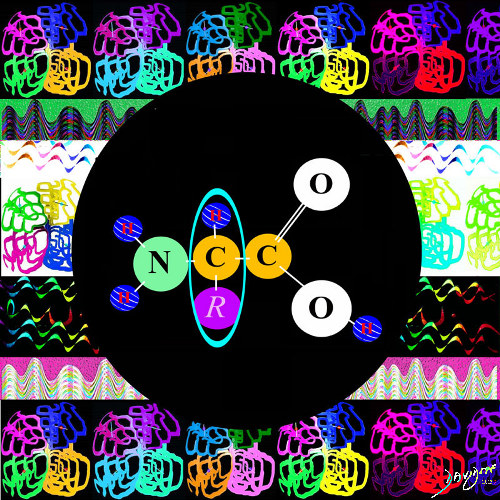
The Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins and Nucleic Acids Combine

+

+

+

=
Organelles
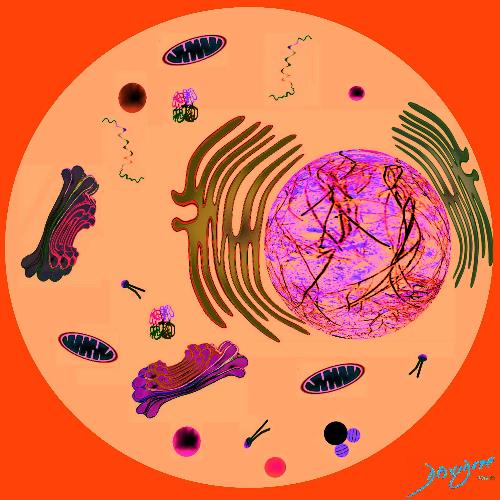



Bond in the Cytoplasm
and Form the Cell
+
Inter-Cellular Bonds
+

=
Tissues
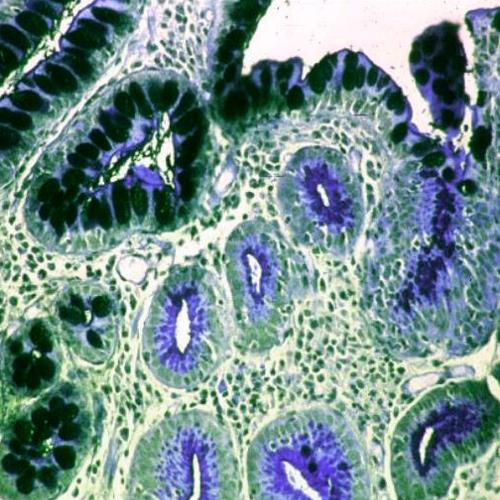
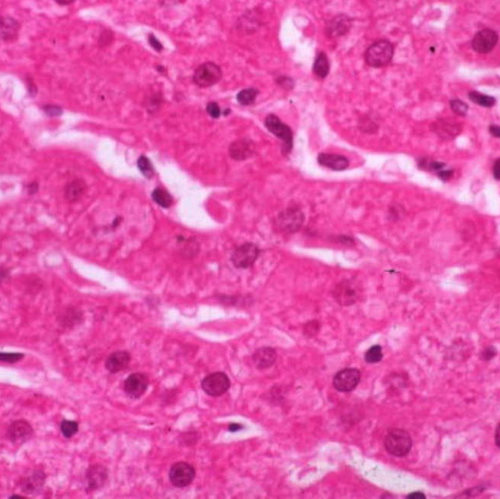
+
Tissue Bonds
+
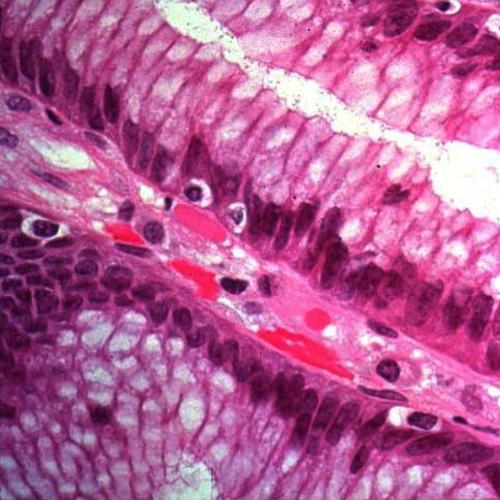
=
Organs
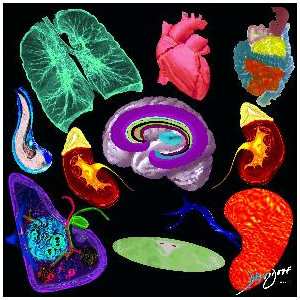
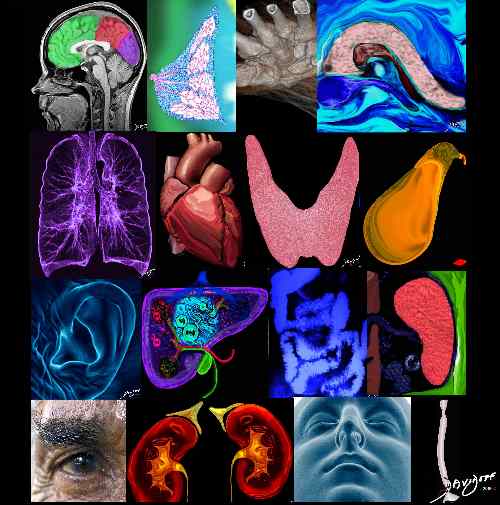
+
Linking Vessels
+
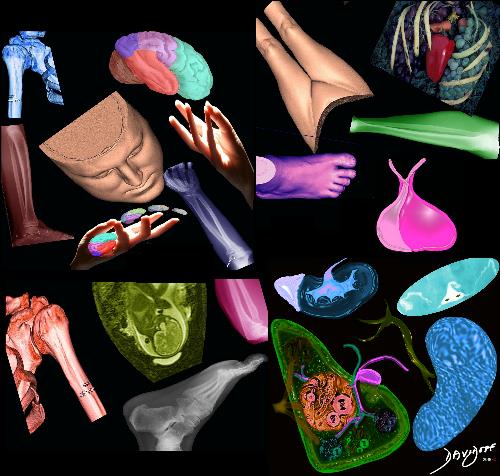
=
Body
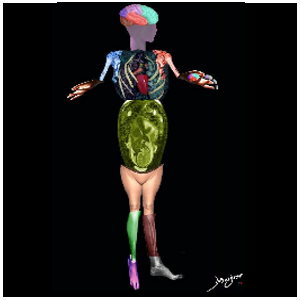
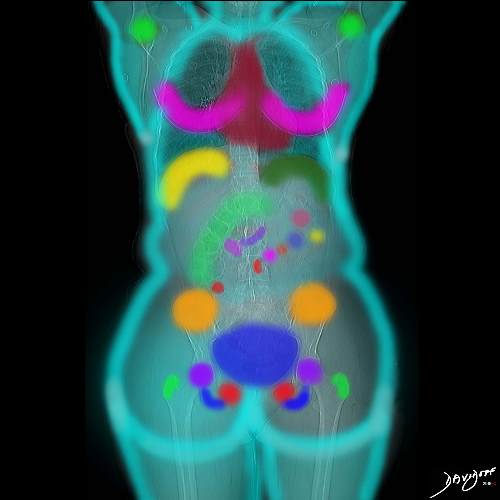
Body-Mind-Bond
=
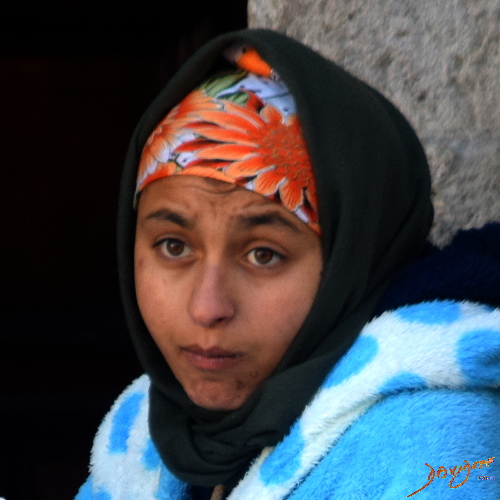


+
Wedding
+

=
Couple
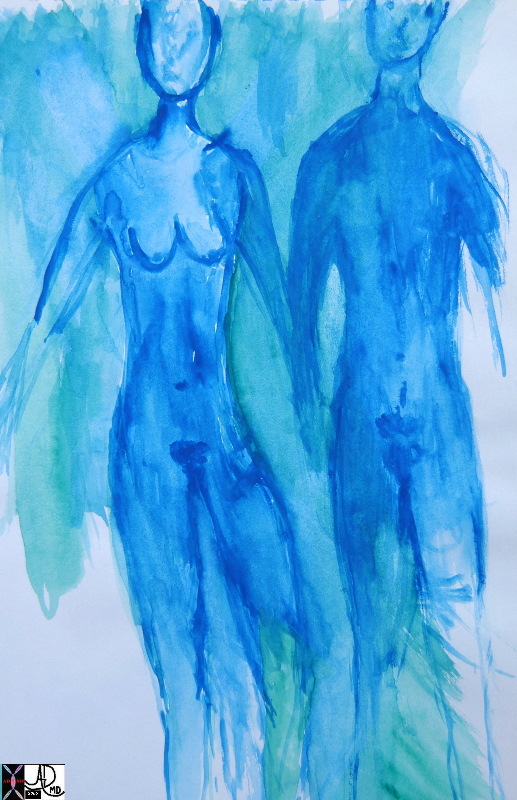


Sexual Bond

=
Family


Families Join

=
Community

Person
+
Family
+
Community
=
Nation
Thus..
The world is driven by units, bonds, and forces that organize in an environment in space and time.